힙(heap) <-> 스택(stack)
힙)
- 런타임에 사이즈가 결정됨. == 동적 메모리
- 데이터베이스 프로그램
- int data[10] -> 실제에는 10개를 더 넣거나 하나만 넣는 케이스가 있을 수 있음.
- 따라서 데이터를 넣을 때만 malloc(sizeof(int))
- 데이터, 객체 등을 생성 -> Memory 생성
- 함수에 종속x
- malloc(할당) - free(해제) 는 세뚜다 세뚜.
자료구조)
- 단일 연결 리스트(Single-Linked-List)
- 포인터에 대한 이해
- 실습 및 1-Day 문제
스택)
- 함수의 지역변수가 저장되는 곳
- ex. SUB RSP, 0x40 <- 사이즈가 고정
- 사이즈가 고정 되는 시점? 컴파일 타임!!@!@!!@
malloc
-----
복습)
BOF
- RET -> 함수 주소로
- 쉘코드 system("bin/sh")
- ASLR : 스택, 힙, 라이브러리
- Fake EBP
- NX : 쓰기 권한과 실행 권한을 동시에 주지 않음
- GOT Overwrite 공격 기법으로 NX 우회
- RELRO 보호 기법으로 GOT Overwirte 방지
- ROP
- NX : 쓰기 권한과 실행 권한을 동시에 주지 않음
이거 해보셈
패딩의 개념 -- 데이터 정렬
다양한 크기의 메모리 할당
- ptmalloc
- 여러 메모리를 할당해서 사이에 있는 데이터를 관찰
- 단일 견결 리스트 구현(같이 할거임)
struct Node {
..?
};
- 가변 길이 문자열 구현
struct Str{
unit32_t len; <- 문자열 길이
char data[1]; <- 문자열 배열(포인터x)
};heap overflow 실습
/*
gcc ./heap_overflow.c -no-pie -o heap_overflow
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ALLOC_COUNT 10
struct Data *allocates[ALLOC_COUNT] = {0,};
struct Data{
uint8_t * ptr;
uint64_t size;
};
void flushbuf(){
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n' && c != EOF);
}
uint32_t findEmpty(){
for(int i = 0; i < ALLOC_COUNT; i++){
if(allocates[i] == NULL){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void allocate(){
int idx = findEmpty();
if(idx < 0){
printf("[-] No empty space\n");
return;
}
struct Data * data = (struct Data*)malloc(sizeof(struct Data));
memset(data, 0, sizeof(struct Data));
allocates[idx] = data;
printf("%p\n", data);
printf("[+] Allocated at %p\n", data);
return;
}
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
void insert(){
uint32_t idx = 0;
char buf[BUF_SIZE] = {0,};
printf("select idx > ");
scanf("%u",&idx);
flushbuf();
if(idx > 9 || allocates[idx] == NULL){
printf("[-] Invalid index.\n");
return;
};
struct Data * data = allocates[idx];
if(data->ptr != NULL){
printf("[-] Data Exists.\n");
return;
}
printf("input > ");
int len = read(0, buf, BUF_SIZE);
data->ptr = (uint8_t*)malloc(len);
memcpy(data->ptr, buf, len);
data->size = len;
printf("[+] Data Inserted!\n");
return;
}
void modify(){
uint32_t idx = 0;
char buf[BUF_SIZE] = {0,};
printf("select idx > ");
scanf("%u",&idx);
flushbuf();
if(idx > 9 || allocates[idx] == NULL){
printf("[-] Invalid index.\n");
return;
};
struct Data * data = allocates[idx];
if(data->ptr == NULL){
printf("[-] Data not exists.\n");
return;
}
printf("input > ");
read(0, data->ptr, BUF_SIZE);
printf("[+] Data modified!\n");
return;
}
void readData(){
uint32_t idx = 0;
printf("select idx > ");
scanf("%u",&idx);
flushbuf();
if(idx > 9 || allocates[idx] == NULL){
printf("[-] Invalid index.\n");
return;
};
struct Data * data = allocates[idx];
if(data->ptr == NULL){
printf("[-] Data not Exists.\n");
return;
}
printf("[+] Data : %s\n\n", data->ptr);
return;
}
void deallocate(){
uint32_t idx = 0;
printf("select idx > ");
scanf("%u",&idx);
flushbuf();
if(idx > 9 || allocates[idx] == NULL){
printf("[-] Invalid index.\n");
return;
};
struct Data * data = allocates[idx];
if(data->ptr != NULL){
free(data->ptr);
}
free(data);
allocates[idx] = NULL;
printf("[+] Deleted!\n");
return;
}
void printSpace(){
printf("\n[Space]\n");
for(int i = 0 ; i < ALLOC_COUNT; i++){
if(allocates[i] != NULL){
printf("[%d] ", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
}
int menu(){
printSpace();
printf("[MENU]\n");
printf("1. Create\n");
printf("2. Insert\n");
printf("3. Modify\n");
printf("4. Read\n");
printf("5. Delete\n");
printf("0. Exit\n");
printf("> ");
int idx = 0;
scanf("%u",&idx);
flushbuf();
switch(idx){
case 1:
allocate();
break;
case 2:
insert();
break;
case 3:
modify();
break;
case 4:
readData();
break;
case 5:
deallocate();
break;
case 0:
exit(0);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void init(){
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
uint32_t flag = 0xdeadbeef;
int main(){
init();
printf("Hello. This is Simple Allocator 2.\n");
while(1){
if(flag == 0x31337){
printf("[!] Oops! You Win!\n");
exit(0);
}
menu();
}
}
메인 함수를 보자.
목표)
flag 값을 변조시키는 것이 최종 목표

BSS : 바이너리 영역. 전역 변수는 BSS에 저장.
코드)
- Create : 전역 배열에 빈 공간이 있으면 할당 및 초기화
- Insert :
- idx 입력받고, 유효한지 검사
- Data 객체가 이전에 쓰인적 있는지 검사
- 최대 1024만큼 입력, len 저장
- len 만큼 할당 및 입력 복사
- Data 객체에 ptr, len 저장
- Modify : 수정
- idx 입력받고, 유효한지 검사
- Data 객체 검사
- Data 객체에 최대 1024 입력 출력
- Read :
- Delete :
Root Cause
- Insert에선 사용자 입력(len)만큼 공간을 할당
- Modify에선 BUF_SIZE만큼 입력 가능하기 때문에 heap overflow가 발생한다.
한계)
- Heap BOF라서 직접적으로 컨트롤 플로우를 변조시킬 수 없음
- 즉, 바이너리 내 기능을 활용해서, flag 값을 변조시키는 방법?을 찾자.
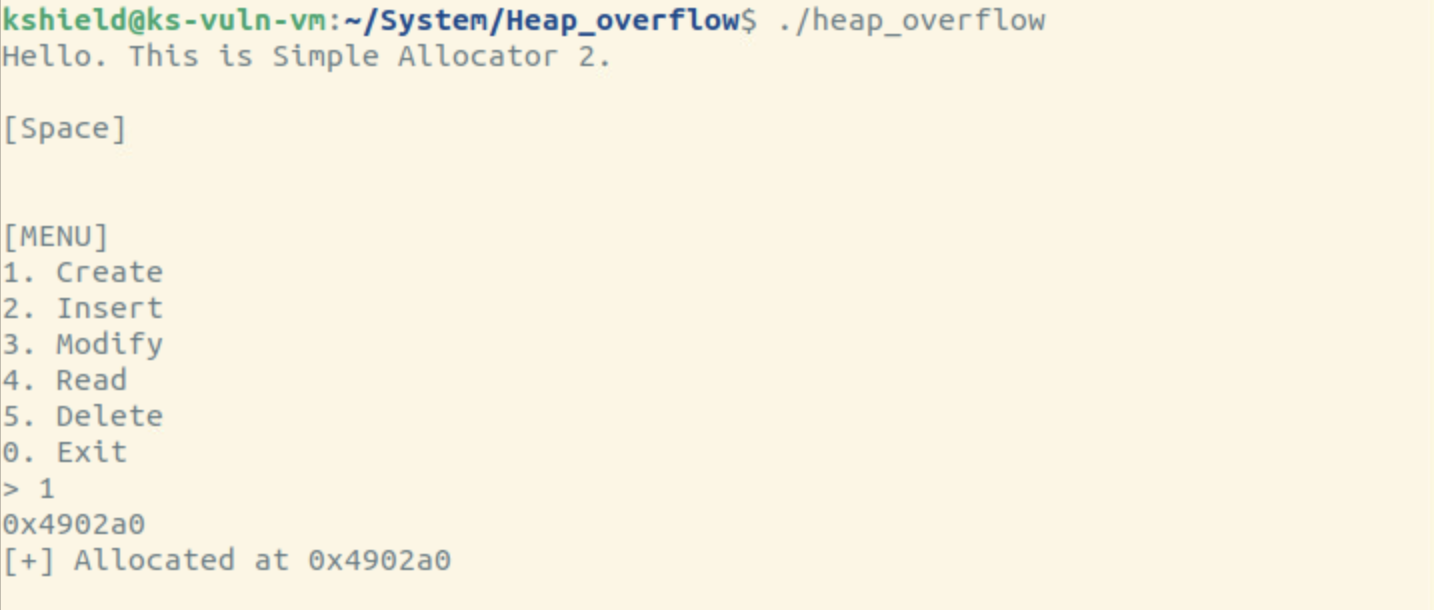
heap_overflow 실행.
1 -> Create 실행. 0번째 인덱스 생성

0번째 인덱스에 "asdf" Insert 진행

0번째 인덱스 값 변경. -> heap overflow 발생시키기 위함.
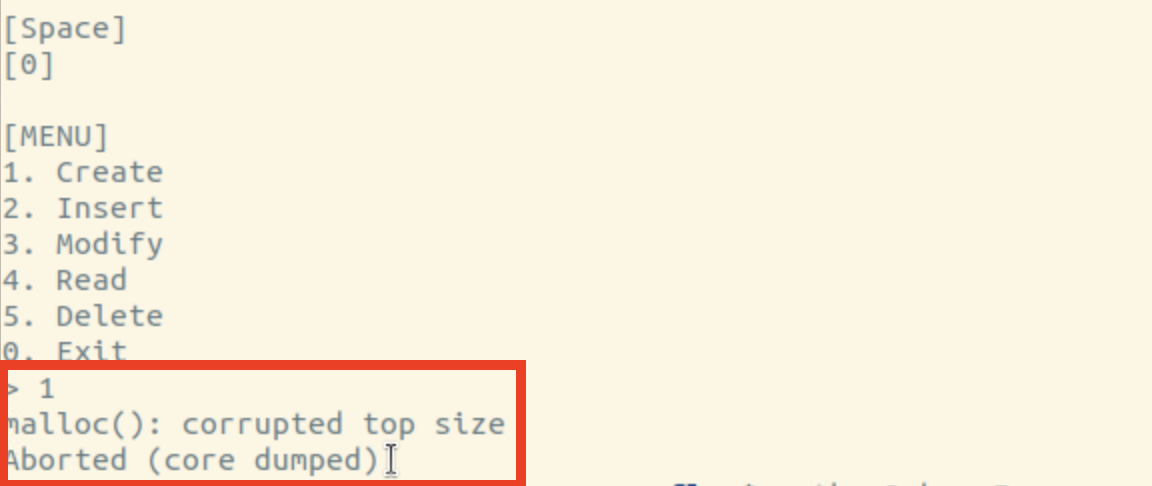
새로운 인덱스 Create 시도 시 에러 발생. -> 강제 종료
Modify에서 data->ptr에 입력받는 것을 이용
1. data->ptr을 flag 변수의 주소로 변조
2. Modify 기능으로 flag 변수의 값 변경
ASLR : 스택, 힙, 라이브러리 랜덤화 <- 운영체제 레벨에서 적용(어지간하면 다 적용되어 있다 생각하면 편함)
PIE : 바이언리 영역 랜덤화
실행한 환경에서 printf 주소 획득 -> libc_printf (= memory leak이라 함)
라이브러리 베이스 ~ printf 까지의 오프셋 계산 -> printf_offset
libc_printf - printf_offset = libc_base
라이브러리 베이스 ~ read 까지의 오프셋 계산 -> read_offset
libc_base + read_offset = libc_read
이런 방식으로 ASLR을 위회한다.
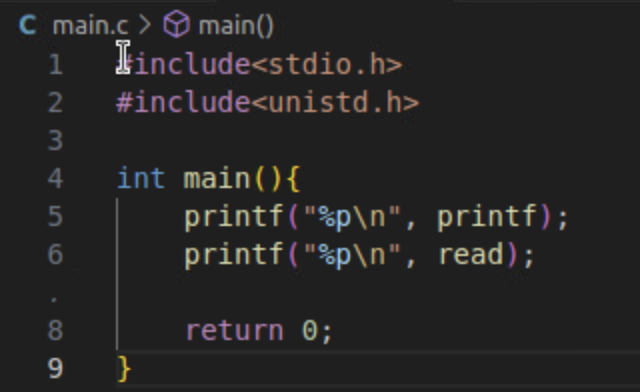
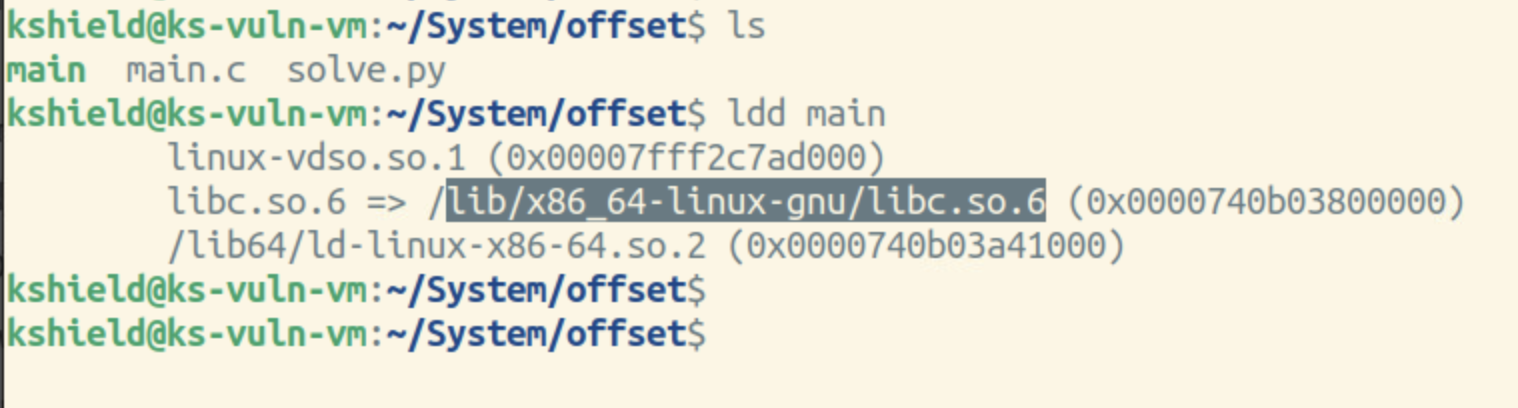
main코드 (offset폴더)

컴파일 진행
끝에 2자리는 같지만 앞자리가 계속 변경되는 것을 보고 ASLR이 적용되어 있다 알 수 있다.
여기까지 heap overflow 마무리.
UAF(Use After Free)
malloc <-> free
free + free -> Double Free Bug
free X -> memory leak(메모리 누수)
free를 여러번 또는 안해도 버그가 남.
해제 후, 포인터 삭제x -> UAF로 이어짐.
참조 카운트(reference count) -- GC
객체가 언제 죽을지 관리해준다.
'K-Shield.Jr' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [취약점분석] 7/26 - 1 Day 실습 시작. (2) | 2024.07.26 |
|---|---|
| [취약점분석] 시스템 해킹 실습 7일차..... (1) | 2024.07.24 |
| [취약점분석] BOF2, Advanced BOF - 7/22 실습 5일차 (0) | 2024.07.22 |
| [취약점분석] BOF(시스템 해킹 실습 4일차) (1) | 2024.07.20 |
| [취약점분석] Type Confusion, Format String Bug(시스템 해킹 실습 3일차) (0) | 2024.07.18 |